Basal Insulin Is Responsible for Which of the Following Actions
Basal-Bolus therapy involves combining a longer-acting or basal insulin analog together with separate injections of a shorter-acting or bolus insulin analog. Due to its duration of action Levemir is considered basal insulin as it provides low concentrations of background insulin that can keep blood sugar stable between meals or overnight.

Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
The duration and actions are not too dissimilar among these insulins.

. Easier blood sugar level management. Correct initiation titration and where appropriate switching between preparations can facilitate good control of FPG. Use of basal and bolus insulin together is intended to mimic the pancreas production of endogenous.
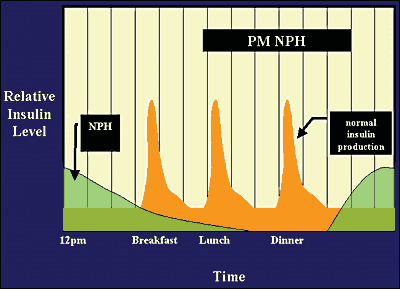
Persons with type 1 diabetes generally use intermediate-acting insulin or long-acting insulin in conjunction with regular or rapid acting insulin. This chart breaks down the types of insulin their duration and the different brands available. Insulin decreases plasma glucose concentration in what three ways.
It also lowers blood glucose by accelerating glycogenesis and inhibiting gluconeogenesis. We have learned a lot about the mechanisms responsible for the regulation of insulin action both at. Generally your total daily dosage of injected insulin is split between these short- and longer-acting kinds.
This discrepancy is due to the incretin effect and is believed to be. Insulin is a protein that is necessary for the metabolism of glucose and a lack of insulin causes an increased level of glucose in the blood and urine. The primary job of basal insulin is to keep your blood glucose levels stable during periods of fasting such as while youre sleeping.
Insulin is a hormone the body makes to control the level of glucose sugar in the blood. Without enough insulin the level of glucose in the bloodstream can become too high. Levels remain more even as basal insulin has no peak time.
Read on to learn more. The mechanism of insulin action is illustrated above. Basal insulin is often combined with short-acting bolus insulin such as Insulin lispro Insulin glulisine and Insulin aspart to provide higher doses of insulin required following meals.
They may also be used in other types of diabetes ie. Reducing production of fatty acids D. The insulinotropic actions of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide GIP and glucagon-like peptide-1 7-37 in normal and diabetic subjects.
Regardless of type of diabetes those needing multiple daily injections will need background insulin basal as well as insulin to cover meals and corrections bolus. Bolus insulin is often combined with once daily long-acting basal insulin such as Insulin detemir Insulin degludec and Insulin glargine to provide low concentrations of background insulin that can keep blood sugar stable between meals or overnight. Increase in fatty acid production D.
It lowers blood sugar by allowing glucose to leave the bloodstream and enter body cells. Increasing glucose concentrations after meals C. The role of basal insulin also known as background insulin is to keep blood sugar levels stable throughout the day and allow your body to take in sugar used for energy for all of the functions needed to support daily life.
Basal insulin is central to many types of insulin therapy and offers several benefits including. Reduction of glucose concentrations after meals C. Patients should be encouraged to self-manage insulin.
Basal insulin is responsible for which of the following actions. Between group differences in the metabolic actions of insulin can occur through alterations at multiple levels including insulin secretion from β-cells insulin delivery and trans endothelial transport insulin receptor expression and signal transduction in the target tissue 1516. Suppressing glucose production by the liver B.
Depending on which delivery mechanism is used the basal can be a long-acting insulin or a rapid-acting insulin while boluses will always be rapid-acting or short-acting insulin more about the. Suppression of hepatic glucose production B. It has the same structure and function as natural insulin.
Everyone needs insulin to use food properly. Basal insulins have greatly evolved from traditional NPH to first generation basal insulin analogues glargine 100umL detemir and now to the next generation of basal insulin analogues glargine 300 umL degludec. Different types of insulin work at different speeds in the body.
Stimulate insulin secretion from beta cells Enhance action of insulin in various tissues Inhibit breakdown of insulin by liver. Basal insulin should also last a full 24 hours in every patient. Increase in ketone production.
2 Its designed to stabilize your. Insulin Human rDNA is human insulin made by recombinant DNA technology. A turning it into ATP protein and fats B uptake of glucose into the cells converting it to glycogen and increasing gluconeogenesis.
Basal insulin is an important component in diabetes management because it acts as a background insulin. Insulin regulates the glucose metabolism and stimulates the ingestion and utilization of glucose by liver muscle and fat tissue. Basal insulin when used correctly is responsible for which of the following actions.
Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst increased hunger frequent urination and weight loss. The main purpose of basal insulin is to control glucose levels in the fasting state which is overnight and in between meals. Basal insulin is longer-acting and helps keep your glucose levels steady day and night.
Intermediate- and long-acting basal insulins are recommended for patients with type 1 type 2 or gestational diabetes. Basal insulin is often required in the management of T2D. The transitions are usually smooth when switching from one branded basal insulin to another.
Despite similar glycemic profiles higher insulin levels are achieved following oral versus intravenous administration of glucose. Therefore the ideal basal insulin should have a steady effect throughout the day and night.
Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Comments
Post a Comment